CT Scan
A CT (Computed Tomography) scan is an essential diagnostic tool and hold immense importance in the medical field providing detailed images of the body's internal structures. This advanced imaging technique uses X-ray technology combined with computer processing to create cross-sectional images, or "slices," of the body. CT scans are particularly useful in detecting various medical conditions, such as tumors, bone fractures, and internal injuries. They can also help guide doctors in planning surgeries or treatments, monitor the progress of a disease, and evaluate the effectiveness of certain therapies. Their non-invasive nature and speed make them an invaluable diagnostic tool in modern healthcare. At Trinity Diagnostics, the CT Scan machine is a state of the art equipment providing precise and reliable imaging.
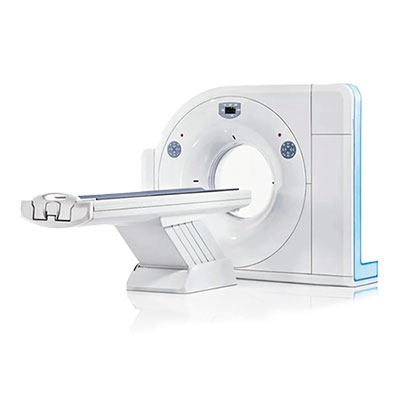

Siemens Somatom 32 Slice
LOGIQ P9 R4
(GE)
Ultrasound Scan
An ultrasound scan, also known as sonography, is a non-invasive diagnostic imaging technique that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of the body's internal structures. This safe and painless procedure is widely used in various medical fields, including obstetrics, gynecology, cardiology, and radiology. Ultrasound scans are particularly useful in examining soft tissues, such as muscles, tendons, and organs, as well as blood flow within blood vessels.
One of the key advantages of ultrasound scans is their affordability and accessibility. They do not expose patients to ionizing radiation, unlike X-rays and CT scans, making them a safer option for repeated imaging or pregnant women. Furthermore, ultrasound scans provide real-time visualization, allowing doctors to observe the movement of organs, blood flow, and even fetal development.
In obstetrics, ultrasound scans play a vital role in monitoring pregnancies, assessing fetal growth and development, and detecting potential complications. Gynecological ultrasounds help diagnose conditions like ovarian cysts, fibroids, or ectopic pregnancies. Cardiac ultrasounds, or echocardiograms, evaluate heart structure and function, while abdominal ultrasounds can detect kidney stones, liver disorders, or gallbladder issues.
X-Ray
X-ray technology, is a widely-used diagnostic imaging technique that produces images of the body's internal structures, particularly bones. X-rays involve the emission of electromagnetic radiation that penetrates the body and creates a two-dimensional image on a detector, such as a photographic film or a digital sensor.
X-rays are non-invasive, relatively quick, and cost-effective, making them an essential tool in medical diagnosis and treatment planning. They are particularly useful for detecting fractures, dislocations, infections, and identifying the presence of foreign objects within the body. X-rays are also valuable in assessing the integrity of bones and joints, monitoring bone growth in children, and examining the chest for lung conditions or bone abnormalities.
X-ray technology has revolutionized the field of medicine by providing valuable insights into the body's internal structures.
ALLENGERS - 300MA.HF
Pathology
Pathology is a branch of medicine that focuses on the study of diseases, particularly their causes, development, progression, and effects on the body. It encompasses the investigation of various aspects, including molecular, cellular, tissue, and organ changes in both healthy and diseased states. Pathologists are medical professionals who specialize in the diagnosis of diseases through the examination of body samples, such as blood, tissue, and other bodily fluids.
There are several subspecialties within pathology, including anatomical pathology, clinical pathology, and molecular pathology. Anatomical pathology involves the examination of tissues and organs to diagnose diseases like cancer, infections, and inflammation. Clinical pathology, on the other hand, deals with the analysis of body fluids, such as blood and urine, to diagnose and monitor various conditions. Molecular pathology is an emerging field that combines traditional pathology with molecular biology techniques. It involves the study of genetic and molecular changes in diseases, allowing for more precise diagnoses and prognoses.
Pathology plays a crucial role in patient care by providing essential information for diagnosis, treatment planning, and disease monitoring. It aids in the detection of diseases at an early stage, enabling timely intervention and improving patient outcomes. Moreover, pathology contributes to medical research, helping to understand the underlying mechanisms of diseases and develop new therapies and preventive measures.
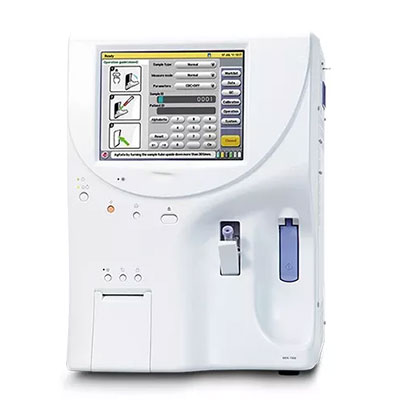
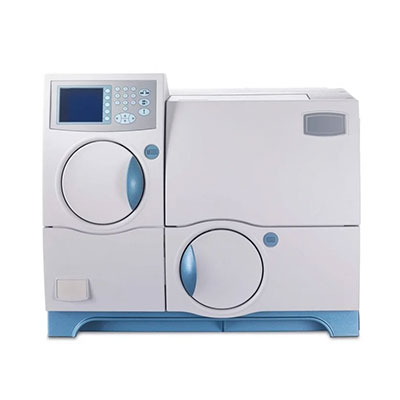
FULLY AUTOMATIC 5 - PART ANALYZER
(NIHON KOHDEN MEK - 7300)
Microbiology
Microbiological diagnostics is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on identifying, detecting, and characterizing microorganisms responsible for various diseases, infections, and conditions. This field plays a vital role in clinical settings, public health, and research, as it enables the accurate identification of pathogens, guiding appropriate treatment and prevention strategies.
Molecular diagnostic techniques have emerged as powerful alternatives to traditional methods. These techniques, such as Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, and gene probes, allow for the rapid and sensitive detection of specific microbial genetic material. This enables the identification of pathogens even in their early stages, facilitating prompt treatment and reducing the risk of disease transmission.
Advanced diagnostic tools, such as mass spectrometry and flow cytometry, offer high-resolution identification and characterization of microorganisms. In recent years, the advent of rapid diagnostic tests, such as lateral flow assays and point-of-care devices, has revolutionized microbiological diagnostics. These tests offer rapid, on-site results, enabling timely interventions and reducing the burden on centralized laboratories.

VITEK 2 COMPACT
(Fully Automated Sensitivity)
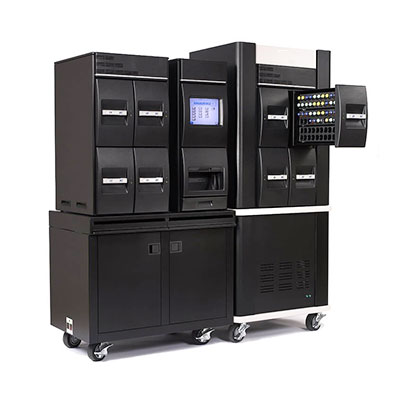

BACT / ALERT 3D
(Fully Automated Cultures)
Advanced Biochemistry
Advanced biochemistry for diagnosis is a scientific discipline that focuses on the application of complex biochemical principles and techniques to identify, measure, and interpret the molecular basis of various diseases and conditions. This field is essential in clinical settings, research, and public health, as it helps in early detection, accurate diagnosis, and tailored treatment strategies.
Several advanced biochemical diagnostic techniques have been developed to analyze the molecular mechanisms underlying diseases, providing valuable information for clinical decision-making. Some of these techniques include:
- Genomics
- Transcriptomics
- Proteomics
- Metabolomics
- Bioinformatics and computational biology
Advanced biochemical diagnostics have significantly improved disease detection, prognosis, and treatment strategies. They have contributed to the identification of novel biomarkers, drug targets, and therapeutic approaches, ultimately enhancing patient care and public health outcomes. As technology continues to advance, the field of advanced biochemistry for diagnosis will undoubtedly play a more significant role in the future of personalized medicine and precision healthcare.
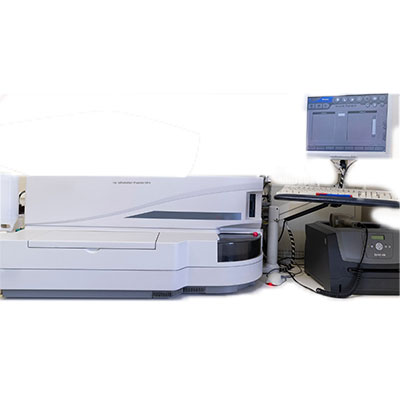

ACCESS 2 IMMUNO SSAY
(BECKMAN COULTER)
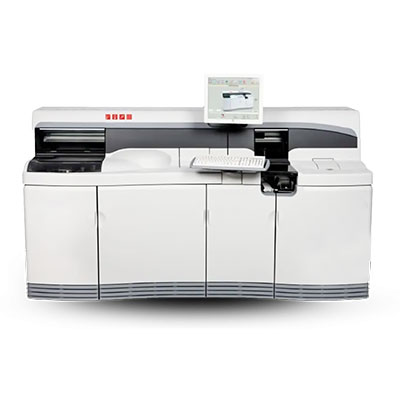

VITROS 4600 DRY CHEMISTRY ANALYZER
(QUIDEL - ORTHO CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS)
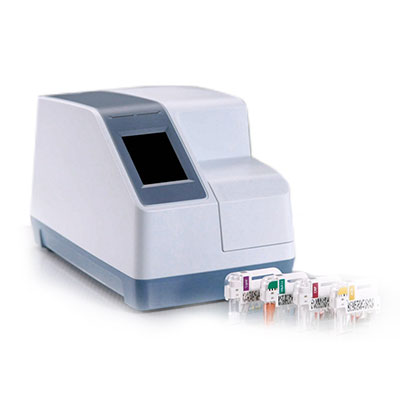

AFINION 2 (HBA1C,CRP,ACR)
(ABBOTT)
Molecular Biology (RT-PCR's)
Molecular biology for diagnosis is a rapidly evolving field that combines the principles of molecular biology, genetics, and biochemistry to identify, analyze, and understand the molecular basis of various diseases and conditions. Several molecular biology techniques have been developed and refined to aid in the diagnosis of diseases, with some of the most prominent methods being:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): A widely used technique for amplifying specific DNA sequences, enabling the detection of even minute amounts of genetic material. PCR is employed in various diagnostic applications, such as detecting viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections, as well as genetic mutations associated with inherited disorders.
- DNA sequencing
- Gene expression analysis
- Protein-protein interaction studies
- Epigenetics
- CRISPR-based diagnostics
Molecular biology has revolutionized the field of diagnosis, enabling early and accurate detection of diseases, guiding personalized treatment strategies, and contributing to the development of novel therapeutics. As technology advances, molecular biology will continue to play a vital role in improving healthcare outcomes and public health initiatives.
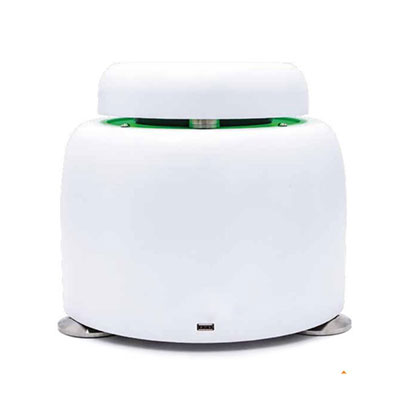

TATA MD CHECK EXPRESS - PCR
Have any Query or Need more Information